

It seems that 18.04 was the last release for 32-bit x86 (i386): https://askubuntu.com/questions/1376090/latest-version-of-ubuntu-for-i386-architecture-32-bit
But you could just go for Debian which still supports it.


It seems that 18.04 was the last release for 32-bit x86 (i386): https://askubuntu.com/questions/1376090/latest-version-of-ubuntu-for-i386-architecture-32-bit
But you could just go for Debian which still supports it.
This seems very one-sided. Sure, the disclosure was not handled perfectly. However, this post completely ignores the terrible response by the CUPS team.
The point on NAT is certainly fair and prevented this from being a much bigger issue. Still, many affected systems were reachable from the internet.
Lastly, the author tries to downplay the impact of an arbitrary execution vulnerabilty because app armour might prevent it from fully compromising the system. Sure, so I guess we don’t need to fix any of those vulnerabilities /s.
This article is conflating terms that I need help distinguishing between. The other commenter mentioned that Ubuntu is a type of Debian but this article lists Debian and Ubuntu as distributions.
I’d say that the article is correct in calling them separate distributions.They are certainly related (both part of the Debian family), but I think most people would consider them to be separate distributions. Software built for Ubuntu 24.04 may work on Debian 12, but it might also not. For a beginner, I think it’s most useful to consider them to be separate things.
I think when I messed it up, it worked when I tried switching to the proprietary drivers for the second time. I think you can try that without much risk.
In my case I ended up disabling Secure Boot anyway because it just got too annoying (a BIOS update breaking it was the final straw for me). The security benefit after you’ve enrolled a MOK seems dubious anyway. It would be nice if distros could ship signed kernels with the open-source Nvidia driver but I guess that’s not happening.


What kind of junk energy is there to harvest from a car (in meaningful amounts)? I guess breaking is the obvious answer, but that’s already covered by regenerative breaking. Most car-based energy harvesting systems seem to employ speedbumps that clearly take useful (kinetic) energy away from the car (probably at a very poor efficiency).


How would a turbine that takes energy from the air current generated by a passing car decrease the energy of the car?
Not sure where you got that idea from, but how would that generate a meaningful amount of energy? It seems very unlikely that such a system would ever recover the energy spent on its construction.


Sure, but those are completely different approaches. Dams have the advantage that they have a much larger capture area for water and that they can accelerate the water beyond the 10 m/s terminal velocity of raindrops.


Raindrop energy harvesting is a rubbish idea. The raindrops simply don’t have a meaningful amount of energy to begin with: https://news.ycombinator.com/item?id=36907674
Did you perform a full shutdown of Windows (Windows doesn’t fully release the partition on a normal shutdown)?
Edit: adding some context. I am planning to setup a dev machine that I will connect to remotely and would like to babysit very little while having stable and fresh packages. In the Ubuntu world we would go to an LTS release but on the RPM/Dnf world is there any other distro apart from CentOS Stream? And also is CentOS Stream comparable to an LTS release at all considering that they do not have release number?
Wanting both stable and fresh packages is unfortunately somewhat difficult in my experience. I think the primary choice within the Fedora ecosystem is if you want to have fresh packages (Fedora) or if you prefer a slower update cycle and more stable packages (RHEL/Alma/Rocky). In the second case you can also choose if you wish to pay Red Hat for support (RHEL) or not (Alma or Rocky).
One thing that’s quite different in RHEL vs Ubuntu/Debian ist that it gets minor releases that include substantial new features. For example you’ll get new compilers, python versions, drivers, … CentOS Stream gets those slightly ahead of RHEL/Alma/Rocky (a cynical person might say that CentOS Stream is a rolling beta for RHEL). But, IMHO that’s not really a strong reason to use CentOS Stream.
If you’d go with an Ubuntu LTS release, then I’d look into RHEL/Alma/Rocky.


The driver should already be installed but there seems to be an issue with brltty registering the corresponding USB ID when they shouldn’t. You can probably fix it by following this guide: https://koen.vervloesem.eu/blog/how-to-stop-brltty-from-claiming-your-usb-uart-interface-on-linux/ (or this one: https://unix.stackexchange.com/a/670637)
Edit: Perhaps this has since been fixed in Mint 21 / Ubuntu 22.04.
You can make this work using ext and Timeshift rsync. I have also opted to exclude /var/lib/flatpak/ because it’s quite large. With that, my 5 snapshots currently take up about 34 GB.
However, I would recommend backing up your deb applications/packages (typically installed under/usr), as those can be critical for your system.
That looks like a software issue… I would try a different distro or a different version of Ubuntu (e.g. 22.04).


Thanks for trying it out on your own system!
In my case, the problem was that the disk never showed up in the Fedora installer. I’ve quickly reproduced the issue in a VM (but I originally noticed it on bare metal):
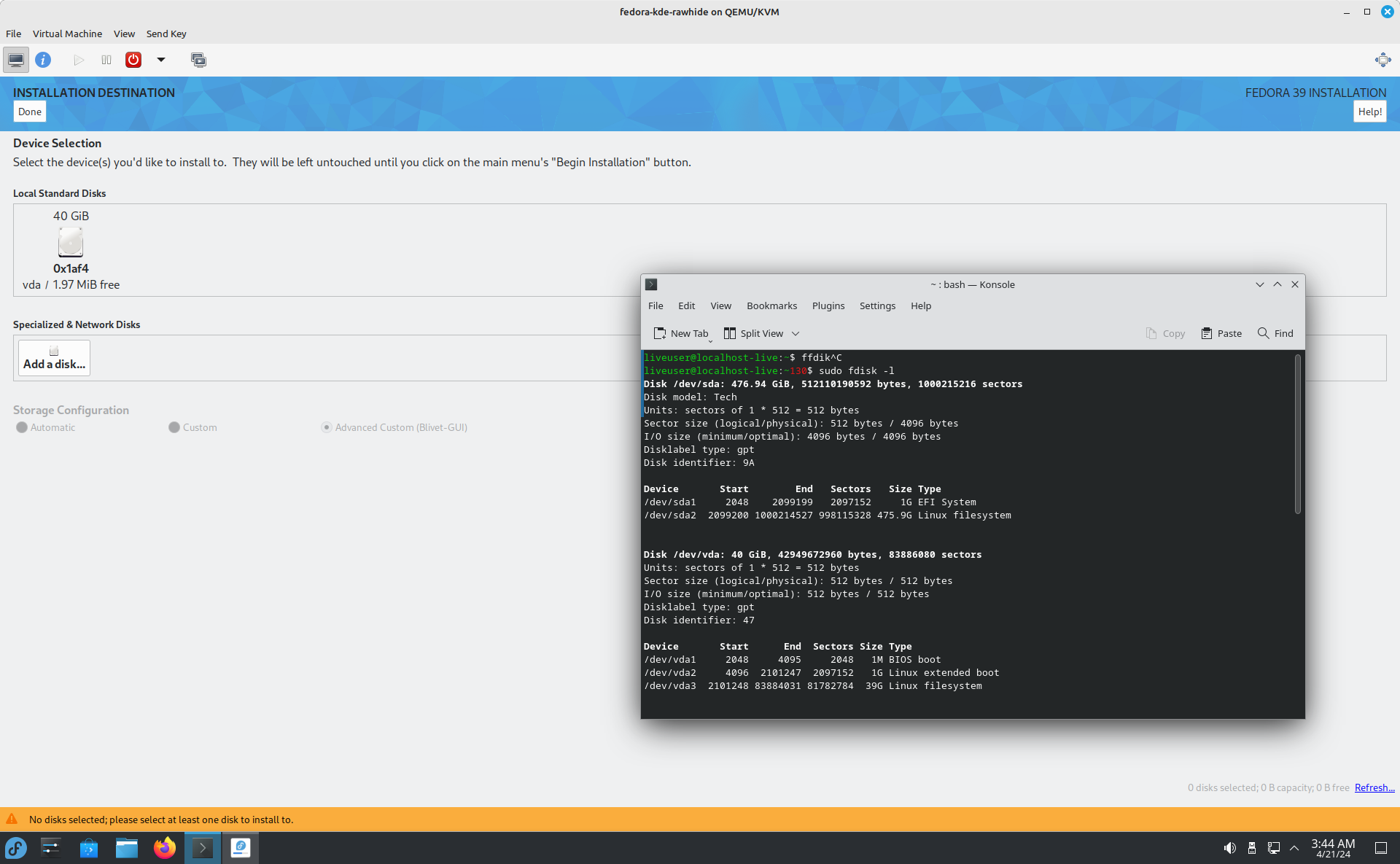
As you can see in fdisk, the disk (/dev/sda) has been recognized correctly by the kernel and works as expected. But somehow the installer only shows the “internal” /dev/vda.
After some further investigation, this seems to be related to the specific USB drives. I tried three different ones. It failed on a USB stick and the original external NVME enclosure. However, it did accept my USB to SATA adapter. So I guess I could install Fedora on my 10-year old HDD… 😐



Did you do anything special to install Fedora it on the USB drive? I couldn’t get it to do that and would be interested in testing F40 that way.


Ah, that would put a bit of complication into things. If you want to actually accomplish this though, you should largely start with the same steps as a standard system install, using a second USB flash drive to write the distro onto the external SSD, leaving enough space to build the rest of the partitions you need.
I’ve actually tried to install Fedora on an USB SSD to play around with it. But somehow the installer just refused to select the second USB drive as an installation target. I looked for quite some time but couldn’t find a way to do it. I ended up trying to install it manually like Arch (for fun), but never got a bootable system 😅 I was able to install Arch and NixOS on the same drive without issue.
I’m actually not sure how OP could achieve something close to what they’re looking for… A regular installation certainly seems like the right choice, but that may require using an internal drive.
Yeah, NTFS being the problem actually makes a more sense.
OP could also just use the fuse driver then. I’m using it on 5.15 (Linux Mint) and it works quite well. I only had problems when I tried to use it for a Steam library.
You could also try to switch the kernel version. Ubuntu 22.04 currently supports two different versions: 5.15 and 6.5, you could switch to the other one and see if the problem also occurs there.
Ah nice, thanks for pointing me to it!
If you don’t want to reinstall the OS, you can probably use Clonezilla: https://clonezilla.org/show-live-doc-content.php?topic=clonezilla-live/doc/03_Disk_to_disk_clone
Maybe you need to update the drive ids for your bootloader (grub) afterwards, not sure about that.
Edit: Maybe the advanced “-g auto” option does that for you.