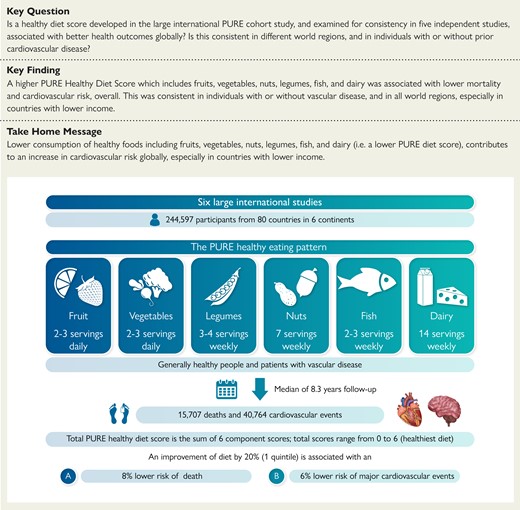
Consuming fruits, vegetables, legumes, nuts, fish and whole-fat dairy products is key to lowering the risk of cardiovascular disease, including heart attacks and strokes. The study also found that a healthy diet can be achieved in various ways, such as including moderate amounts of whole grains or unprocessed meats.
The World Health Organization estimates ~18 million people died from cardiovascular disease in 2019, representing 32% of all global deaths. Of these deaths, 85% were due to heart attacks and strokes. Population Research Health Institute researchers and their global collaborators analyzed data from 245,000 people in 80 countries from multiple studies.


While taking issue with p-values is a valid stance, the paper uses confidence intervals and bayesian methods (cubic splines) in addition to p-values, both of the proposed alternatives in the ASA’s statement that you mentioned below.
While p-values are listed, there’s stats which fall in line with the recommendations in this very paper. If you take issue with either of these methods, could you help explain to me why you’re upset? Or is it just the fact that p-values are stated rather than focusing on the CI and bayesian results? I personally think there’s value to still showing a p-value because it makes it slightly more approachable to the non-scientific or statistical crowd, so long as it’s not used to distract from poor fit of other models.
No, that’s my bad, thank you for correcting me! I only read the abstract, and they don’t mention Bayesian methods there. Confidence intervals suffer from similar flaws as p-values and statistical significance.
It’s great that they do analyses with other methods too indeed. Not, from my point of view, because they’re more approachable – quite the opposite: people think in terms of probabilities-of-the-hypotheses, and p-values are not that (that’s one source of their misuse). But because it helps the transition to other methods. It’d been nice if they had stated the results from all methods in the abstract. But that’ll be for next time maybe!
Cool thanks for clarifying! While I am a data scientist I am not a stats expert so always looking to understand proper critiques from those more knowledge than me 😄
Thank you for the correction. Don’t trust me, though: check out the proofs and discussions in the references here, see for yourself :)